Abstract
Introduction: Amphiregulin (AREG) is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ligand that can restore integrity to damaged intestinal mucosa in murine models of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD). We previously described AREG as a circulating biomarker of late-onset aGVHD, but its relevance combined with clinical risk factors has not yet been tested in a large cohort of patients with aGVHD occurring prior to day 100 post-transplant. We therefore tested samples from two aGVHD first-line treatment trials, Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) 0302 and 0802, and identified a clinically relevant threshold level of circulating AREG at aGVHD onset. We then investigated whether incorporating AREG into the refined Minnesota Risk Score could further risk-stratify patients.
Patients and Methods: Blood samples were obtained at the onset of systemic aGVHD treatment within BMT CTN 0302 (serum) and BMT CTN 0802 (plasma). All patients with response data and samples for analysis from both trials were included (N=251). We determined the association of AREG with clinical outcomes, including risk stratification by the refined Minnesota criteria, day 28 complete/partial response (CR/PR) to first-line therapy, 2-year overall survival (OS) and 6-month and 2-year non-relapse mortality (NRM). We investigated the effect of AREG on clinical endpoints per a doubling in the value of AREG, defined a clinically relevant threshold level in the AREG values using two-fold cross-validation, and confirmed the clinical relevance of this cut-point in independent samples (N=92) from pooled from drawn from the Chronic GVHD Consortium and the Mount Sinai Acute GVHD International Consortium (MAGIC).
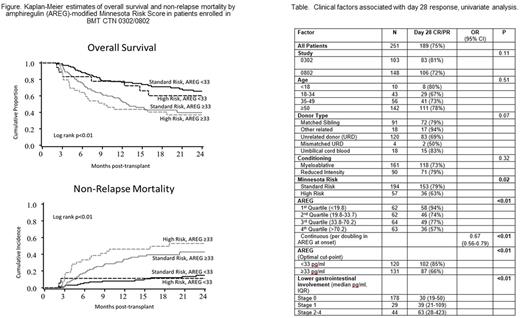
Results: In patients enrolled in BMT CTN 0302/0802, AREG levels were 1.7-fold higher in patients with Minnesota high-risk (HR) compared to standard-risk (SR) aGVHD (HR median 53.4 vs SR 31 pg/ml, p<0.01). Every 2-fold increase in AREG was associated with a 33% decrease in the likelihood of day 28 CR/PR (odds ratio [OR] 0.67, p<0.01, table). Clinical factors alone, as determined by the refined Minnesota Risk Score, were associated with day 28 CR/PR (p=0.02, table). Adding AREG to the Minnesota Risk Score could further risk-stratify patients. Minnesota SR patients with elevated AREG ≥ 33 pg/mL showed a 59% lower odds of day 28 CR/PR than SR patients with low AREG (OR 0.41, p=0.02). Patients with Minnesota HR aGVHD with AREG ≥ 33 pg/mL had the worst outcomes, with an 82% lower odds of day 28 CR/PR in comparison to HR with low AREG (OR 0.18, p<0.01). High AREG was associated with worse OS and NRM in both Minnesota SR (hazard ratios 2-year OS 2.3, p<0.01 and 6 month NRM 2.95, p=0.01, respectively) and HR patients (hazard ratios 2-year OS 3.35, p<0.01 and 6-month NRM 9.38, p<0.01 respectively, figure). Finally, in independent samples from the Chronic GVHD Consortium/MAGIC we confirmed that high AREG was associated with worse day 28 CR/PR (55.2% vs. 79.4%, p=0.02) and significantly worse 6-month survival after the onset of aGVHD (57.1% vs. 82.5%, p=0.01).
Conclusion: AREG is elevated in patients with poor aGVHD outcomes and adds to the accuracy of risk stratification when combined with the refined Minnesota Risk Score. AREG ≥33 pg/mL at aGVHD onset is associated with lower day 28 CR/PR and higher mortality in samples from 4 multicenter cohorts. The mechanism of elevated circulating AREG in severe aGVHD is not yet known, although we hypothesize the degree of AREG elevation reflects the intensity of immune-mediated tissue injury resulting in AREG release. With accumulating evidence of altered EGFR ligands in aGVHD, further investigation into epithelial repair pathways involving AREG may lead to new adjunctive therapies to overcome poor steroid response in high-risk aGVHD.
Holtan: Incyte: Other: One-time advisory board member. Khera: Novartis: Consultancy. Lee: Mallinckrodt: Honoraria; Amgen: Other: One-time advisory board member; Bristol-Myers-Squibb: Other: One-time advisory board member; Kadmon: Other: One-time advisory board member. Chen: Immudex: Research Funding. Arora: Takeda Oncology: Consultancy. Flowers: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Cutler: Pfizer: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy. Jagasia: Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Therakos: Consultancy, Research Funding; Mallinckrodt: Consultancy. Hexner: Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Levine: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. MacMillan: Magenta Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal